This is a much longer update of a previous post on mortgage debt forgiveness. There is an earlier post here which led to an appearance as yet another talking head on the television. (There is short report at the start and yours truly butts in from 8:30 on).
This post covers a number of themes:
- Analysis of mortgage loss figures in the bank stress tests
- Analysis of mortgage arrears data from the Financial Regulator
- Likely levels of default and losses in the mortgage market
- The extreme costs of a debt forgiveness scheme
- The limited benefits of a Deferred Interest Scheme
- Proposal for a Shared Interest Scheme to assist those in difficulty
As this suggests there is quite a lot to this post but I hope it can contribute a little to what should be a very important debate in Ireland. Recently we have been transfixed by the projected levels of public debt we might have but we cannot forget the actual levels of private debt we do have, particularly of households.
There have been numerous predictions of meltdown in the mortgage market and the recent stress tests on the banks have incorporated this view. The projected mortgage losses will lead the nationalisation of yet another bank. Losses at the levels estimated are unlikely to occur but steps need to be taken to help the thousands of households who are struggling under the weight of massive mortgage debt and to allow a fresh start for those who are in positions that are impossible to recover from.
The latest figures from the Financial Regulator show that there are just over 780,000 mortgages outstanding in Ireland for owner-occupied homes and that the total balance owing on these is about €116 billion. The average mortgage balance in Ireland at the end of March 2011 was €148,200.
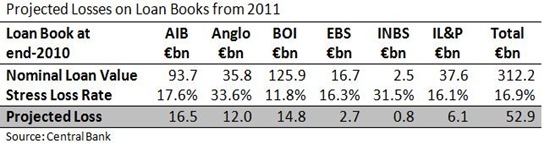
The recent stress test documents show that the four “viable” covered banks (AIB, BOI, PTSB and EBS) account for €74 billion or 63% of the outstanding owner-occupied mortgages. There are around €20 billion of residential mortgages in each of AIB, BOI and PTSB with EBS accounting for another €14 billion. The remaining €43 billion of Irish mortgages originated from INBS, non-covered banks such as Ulster Bank, National Irish Bank and Bank of Scotland, and various sub-prime lenders.
Of the €74 billion of residential mortgages analysed in the stress tests, BlackRock Consultants estimate a total loss of €10.2 billion, or a loss rate of 13.7%, for the adverse scenario over the full lifetime of the loan book. The Central Bank forecasts that €5.6 billion of these losses will occur in the next three years.
Based on these mortgages losses, but mainly because of €35 billion of projected losses on other parts of their loan books, the Central Bank has required the four banks to raise €24 billion of additional capital. Most of this will come from the State. The other projected losses covered by recapitalisation by the State also includes estimated losses of €6 billion on the €23 billion of buy-to-let mortgages the four banks hold.
Is it any wonder that the chairman of AIB, David Hogdkinson, proposed a possible debt-forgiveness scheme for its mortgage holders, when the bank is getting money to cover almost €2 billion of mortgage losses over the next three years? It is easy to be generous with other peoples’ money and this is taxpayers’ money.
For PTSB the estimated lifetime loss on owner-occupied mortgages is 15.3%. Nearly 90% of the total stress test losses for PTSB come from residential property. There is a lifetime loss rate of 31% applied to PTSB’s buy-to-let loan book. PTSB does have problems with the low-cost trackers but these are huge loss rates which only widespread default can produce.
Based on these projected mortgage losses of €1.1 billion, €2.2 billion of losses on the firesale “non-core assets” (mainly PTSB’s performing UK loan book of €10 billion), and a €0.7 billion capital buffer, the Central Bank has imposed a capital requirement of €4 billion for PTSB. This will see the Irish Life and Permanent group broken up, with the Irish Life pensions and insurance business sold off and PTSB being nationalised. The shareholders of IL&P are being wiped out because of the mortgage losses estimated by BlackRock in the stress tests and the imposed firesale or other assets. Will they get their company back if these losses do not materialise?
If the same average loss rate estimated for four covered banks in the stress tests is applied to the entire residential mortgage market in Ireland, lifetime losses of €16 billion are envisaged on the €116 billion of mortgages, with €9 billion of losses occurring before the end of 2013. Some of these losses arise because the rate on most tracker mortgages is lower than the average funding costs of the banks. However, the covered banks are accessing almost €80 billion of funding at the ECB’s base rate and all tracker rates are a fixed margin above this. We are not concerned about the funding costs of the non-covered banks.
When a bank forecloses on a mortgage and takes possession of the house they can use the value of the house to offset some of the outstanding balance on the defaulted mortgage. The losses estimated by BlackRock are defined as “the principal loss amount crystallised at the time of property liquidation”. We need to know how many mortgages need to default in order for these €16 billion of losses to materialise.
If we assume that these liquidations will allow the banks to recoup just 40% of the unpaid loan amount then the total level of defaults in the Irish mortgage market are estimated to be €27 billion. From these defaults the banks would have property worth €11 billion and would be left nursing losses of €16 billion. The assumption of a 40% recovery based on the value of the property is likely to be low but would probable not be more than 60%.
Based on the average loan figure given above this means total default on about 180,000 mortgages, with 100,000 defaults over the next three years. It is likely that the balance on defaulting mortgages will be higher than the €148,000 average across the entire market. If we assume that the defaulting mortgages are 50% greater than the average the losses laid out above require 120,000 defaults on mortgages of around €225,000.
Are 100,000 people about to default, in full, on their mortgages? Not likely.
The data from the Financial Regulator show that 49,600 mortgages are in arrears of three months or more. This has been increasing by 4,000 per quarter since the regulator began to publish the statistics in late 2009. These people cannot pay their mortgage now, but there is no indication that all of these people, and more nearly twice as many again, will never be able to pay them.
There are also nearly 63,000 mortgages that have been restructured. Of these, 26,000 are also in arrears so are in the above totals. Just over 36,000 mortgages have been restructured and this has helped to avoid arrears in these cases. About a third of these have moved to interest-only payments with a quarter changing to a reduced payment.
The remaining restructures include term extensions, arrears recapitalisation and a payment moratorium for a small number of cases. The number of mortgages in arrears or restructured make up about 11% of the total. The vast majority of people are meeting their mortgage obligations. Nine out of every ten mortgages are being repaid according to the terms laid out in the original contract. It is also worth noting that in 2010 the total amount of residential mortgage debt reduced by €1.7 billion and the number of mortgages declined by nearly 7,000.
The total outstanding balance on the 49,600 mortgages in arrears is €9.6 billion or an average of €193,500. This might suggest that the €14 billion of mortgage defaults before the end of 2013 based on the stress test estimates is not too wide of the mark. However, mortgage arrears and mortgage defaults are not the same thing.
The arrears owing on these mortgages is around €825 million or about €16,700 per mortgage in arrears. It is hard to see 100,000 full defaults materialising by the end of 2013 when the 49,600 currently in arrears are behind in their payments by an average of €16,700.
In most cases it is the specific problem of these arrears that needs be addressed. In many cases the mortgages are unsustainable and will never be repaid. It is important that a distinction is made between those mortgages which can’t be paid now and those that can never be repaid. These are two massive problems but they should not be addressed with the same solution.
It is not necessary to introduce a solution that could see €40 billion of mortgage debt forgiven. Somebody will have to pay this €40 billion. The problem is that those in arrears cannot pay their mortgages now but the debt-forgiveness solution is only appropriate if they can never pay them. This is undoubtedly going to be true for some people in arrears, but it will not be true for all of them. The big problem is distinguishing between these two groups.
The Department of Social Protection already runs a mortgage relief scheme for families with low incomes. The Mortgage Interest Supplement (MIS) ensures the full mortgage interest is paid for almost 18,000 households. It is not clear if there is significant overlap between the households being assisted by the MIS scheme and those included into the mortgage arrears statistics produced by the Financial Regulator. While the MIS scheme is useful it only applies to households on low incomes. In the current environment, a scheme for all those having severe difficulty paying their mortgages is necessary.
The Expert Group on Mortgage Arrears chaired by Hugh Cooney published its findings last November and proposed a Deferred Interest Scheme. This proposal does not go far enough but an outright debt forgiveness scheme goes too far.
An article signed by 11 economists published by this paper in November 2010 proposed a debt resolution regime with a “writedown of at least 30 per cent of the more recent mortgage amounts on average, yielding an expected total cost to the entire system of circa €37 billion to €49 billion”. The article did not explain how the scheme would distinguish between the two-thirds of mortgages in the covered banks and the one-third in other banks, but this huge burden would ultimately fall on the State.
How big is the problem? This is hard to determine but as an estimate assume that half of mortgages now in arrears are unsustainable and will never be repaid. This would be 25,000 mortgages and will we further assume an average balance of €250,000. This means there would be about €6.25 billion of unsustainable mortgages in the system. If 50% of the balance of the loan can be recovered through repossession then we are looking at a problem for the bank of around €3 billion. We do not need a €40 billion solution to a €3 billion problem.
A general debt-forgiveness scheme does not have much to offer in the current climate and presents more problems than solutions. Should those people, who have borne the cost of their mortgages, lose out simply because they have committed their money to paying their mortgages rather than using it elsewhere? Can we equitably discriminate between those people who have met their mortgages payments and those people who have not? Can we fairly ask those who saved for deposits before buying a house and have made their repayments to pay the mortgage of their neighbour who took out a 110% loan and has only been making interest-only payments?
It is very hard to see how the benefits of a debt-forgiveness scheme can exceed the costs. We cannot simply magic away the debt. A debt-forgiveness scheme will simply transfer individual private debt to social public debt that the Irish State still carries. The country will still have the same aggregate debt burden but we will have just changed who will have to pay it. Any increase in spending by those who benefit from the scheme will have to be offset by increased taxation on those who have to pay for it.
The NAMA process saw the banks involved take a €40 billion write-down on the developer loans they transferred to NAMA. This €40 billion hole was filled by huge transfers from the State. We do no need to create another €40 billion hole to be filled in the balance sheets of the banks.
The immediate problem to be addressed is mortgage arrears not negative equity. For many mortgage holders negative equity is a medium term state that has little real impact. It is a problem for those who wish to move or sell. The proposals here deal with those who are struggling to repay their mortgage rather than those who are simply in negative equity. These will obviously be over-lapping groups but a general debt-forgiveness scheme for those in negative equity is not recommended.
Similar to the Expert Group, any solution should be based on interest relief rather than capital forgiveness. The solution must lighten the load on those who are currently smothered by debt and need some room to manoeuvre. The Deferred Interest Scheme offers some temporary relief but within five years the deferred interest will be added back to the principal and the individual is expected to make repayments on this now larger loan.
A debt-forgiveness scheme is too generous because it makes the loan smaller and forces someone else to pick up the bill. The Deferred Interest Scheme is too unforgiving because it makes the loan larger and forces the individual to repay even more. We need to find a scheme that gets the balance just right. Here is one proposal.
The covered banks can use the money they are getting from the State to pay the interest on a portion of the loan for a certain period for those with payment difficulties. For the non-covered banks the State will have to provide money to cover the interest on a portion of the mortgage. This would impose a cost on the State in a time of huge fiscal difficulty, but we need to offer something tangible to those who find themselves in dire straits.
The other portion of the loan will stay with the individual. At a minimum they will have to meet the interest on that amount and will hopefully be in a position to make some capital repayments. The individual continues to have the incentive to repay as much as they can but on a much smaller balance. If they cannot met the interest payments on 50% of the loan it is likely necessary that the loan be classified as unsustainable, a debt resolution process should be initiated and the mortgage terminated.
This interest-sharing scheme offers some help to those in need but avoids shifting the burden of the capital repayment around. So, for some mortgages the household would be free of the interest costs of up to 50% of the loan for a certain period of time. There will be some cost to the State but nothing approaching €40 billion.
In the unlikely event that all the €27 billion of mortgages estimated to default under adverse scenario of the stress tests enter this scheme, the maximum annual interest cost to be carried would be around €600 million. Two-thirds of this would be in the covered banks that are already getting money to meet losses on these mortgages. The maximum additional extra cost to the State would be around €200 million per year and this is likely to be an upper estimate. As will be shown below after three years this will begin to reduce.
Once the burden of servicing the mortgage has been shared to give these people some breathing space we need some process that sees the responsibility move back to the individual borrower.
One serious flaw with a debt-forgiveness scheme is that people position themselves to benefit from it. If people expect a bailout they will go into arrears on their mortgage, fall behind on their utility bills and squirrel away any savings they have. This is nothing to do with moral hazard; it is simply the power of incentives.
It has nothing to do with moral hazard because those who are facing a mountain of debt are unlikely to want to be in this stomach-churning situation again. Those who have avoided the debt glut this time around are unlikely to be encouraged to over-borrow in future because of a partial debt-forgiveness scheme now. Incentives have the power to ruin a debt-forgiveness scheme.
Incentives can also be used in a positive fashion. Just think of the impact of the plastic bag levy. In this instance the scheme should extend, to say, 13 years but the individual decides when the mortgage moves back to them.
If they do so after three years they just take it back under the original conditions. For every year after that the interest rate on the loan increases by some incremental amount. For example there could be a 10% proportionate increase in the rate. This extra interest does not go to the banks, covered or non-covered, but goes to the State for providing the scheme in the first place.
Consider an individual with a €200,000 mortgage and an interest rate of 5%. They are under extreme pressure to meet the repayments on this loan and it is decided that 50% or €100,000 of their loan will enter the Shared Interest Scheme.
The €15,000 interest cost on this €100,000 for the first three years will be covered by the scheme. If they leave the scheme at this point they assume responsibility for the €100,000 at their original mortgage rate. Over another 20 years they would repay the capital plus €58,000 interest on the €100,000 and would have received a €15,000 benefit from the scheme.
If they choose to stay in the scheme after the first three years they will start to incur additional interest costs. If they leave after the fourth year the rate rises by 10% so they would be paying 5.5% over the lifetime of the loan. Now over 20 years they would repay the capital plus €65,000 in interest on the €100,000.
Although, the Shared Interest Scheme offers a short-term benefit to the borrower, the borrower is incentivised to leave the scheme as early as possible to avoid paying excessive penalty interest. There is no penalty for the first three years of interest sharing and in the example used here, the borrower gains €5,000 from the interest-sharing for the fourth year but pays back an extra €7,000 over the 20-year term of the loan.
The benefit to the individual of participating in the scheme for four years is €13,000. This is the €20,000 of interest covered by the scheme over the four years minus the €7,000 of extra interest incurred by staying in the scheme beyond the ‘free’ three years.
In each year after year three at least 10% of the amount in the interest-sharing scheme must move back to the individual. The penalty interest will encourage them to take more but if they cannot manage this extra portion the loan should be declared unsustainable.
The longer a person needs support from the scheme the more they will have to pay. If they wait the full 13 years, the penalty interest will be double the original loan rate. This would only apply to the portion of the loan on which they benefitted from the interest-sharing scheme for the full 13 years. There would be lower proportionate increases for the money moved out of the scheme earlier.
These numbers and time periods are only for illustrative purposes and it is likely that anomalies can be found in the simple example used here but it does show how such a scheme might work. It may not appear to be a very straightforward system but this is not a problem to which a “sound-bite solution” is likely to be effective.
A lot can happen over a period of five, eight or ten years. It may seem improbable now but even economic growth, job creation, inflation and the like can happen. A mortgage is a long term contract that can extend to 25 or more years. We don’t need a short-run solution (immediate debt-forgiveness) to what is a long-run problem (repaying a mortgage). We also do not need a debt-forgiveness scheme run by our delinquent banks. We need to address the problem in a realistic fashion and offer help to those that need it without placing an unnecessary burden on everyone else.